Magnesium for Mental Health As challenges rise globally, more people are turning to natural remedies and nutritional solutions to support emotional well-being.
One mineral gaining attention in the scientific and wellness community is magnesium. But the question remains: Does magnesium really help with anxiety and depression?
Let’s explore the research, benefits, and practical ways to incorporate magnesium into your mental health routine.
🧠 The Role of Magnesium in Brain Function
Magnesium is involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the human body, many of which affect brain function. It regulates neurotransmitters, influences hormone activity, and supports nerve cell communication.
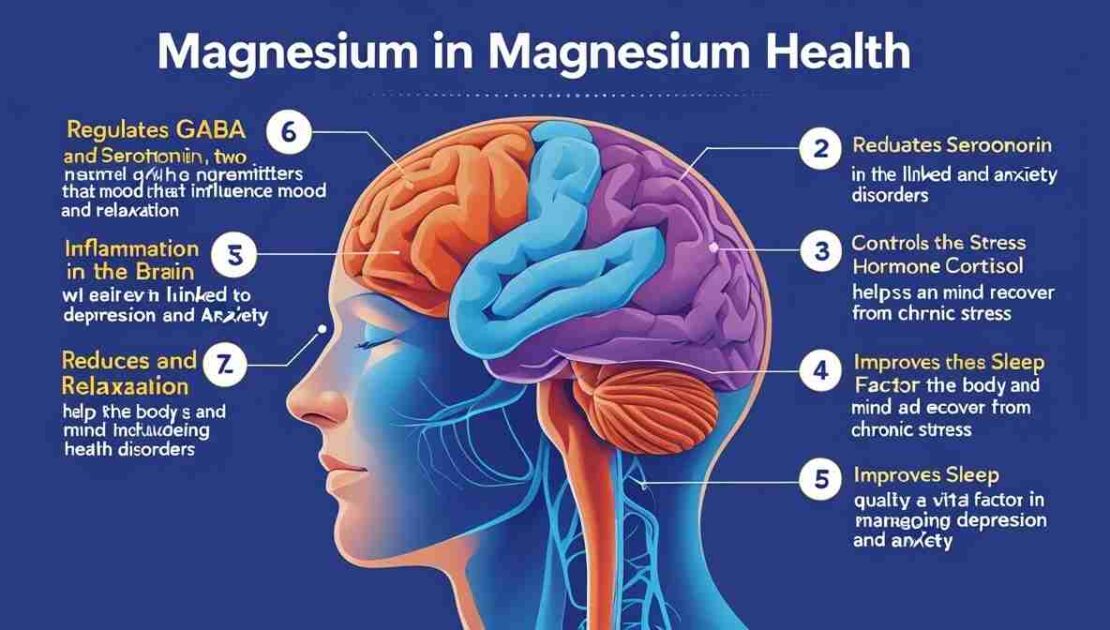
Key Functions of Magnesium in Mental Health:
- Regulates GABA and serotonin, two neurotransmitters that influence mood and relaxation
- Reduces inflammation in the brain, which is linked to depression and anxiety disorders
- Controls the stress hormone cortisol, helping the body and mind recover from chronic stress
- Improves sleep quality, a vital factor in managing depression and anxiety
Studies have shown that people with depression and anxiety often have lower magnesium levels compared to healthy individuals.
🌿 How Magnesium Helps with Anxiety and Depression
1. Magnesium and Anxiety Relief
Research suggests magnesium may act as a natural calmative, blocking the stimulation of glutamate—a neurotransmitter linked to anxiety. It helps activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes rest and relaxation.
Related Reading: Self-Care Routines for Anxiety
These routines, combined with magnesium intake, may offer a powerful solution for managing daily stress.
2. Magnesium and Depression Management
Low magnesium levels are associated with an increased risk of depressive symptoms. One clinical trial found that magnesium supplementation improved symptoms of depression in as little as 6 weeks, even without antidepressant use.
Magnesium may also be helpful for depression linked with chronic stress, hormonal imbalances, or nutrient deficiencies.
Related: Mindful Mental Health: A Path to Reduced Inflammation
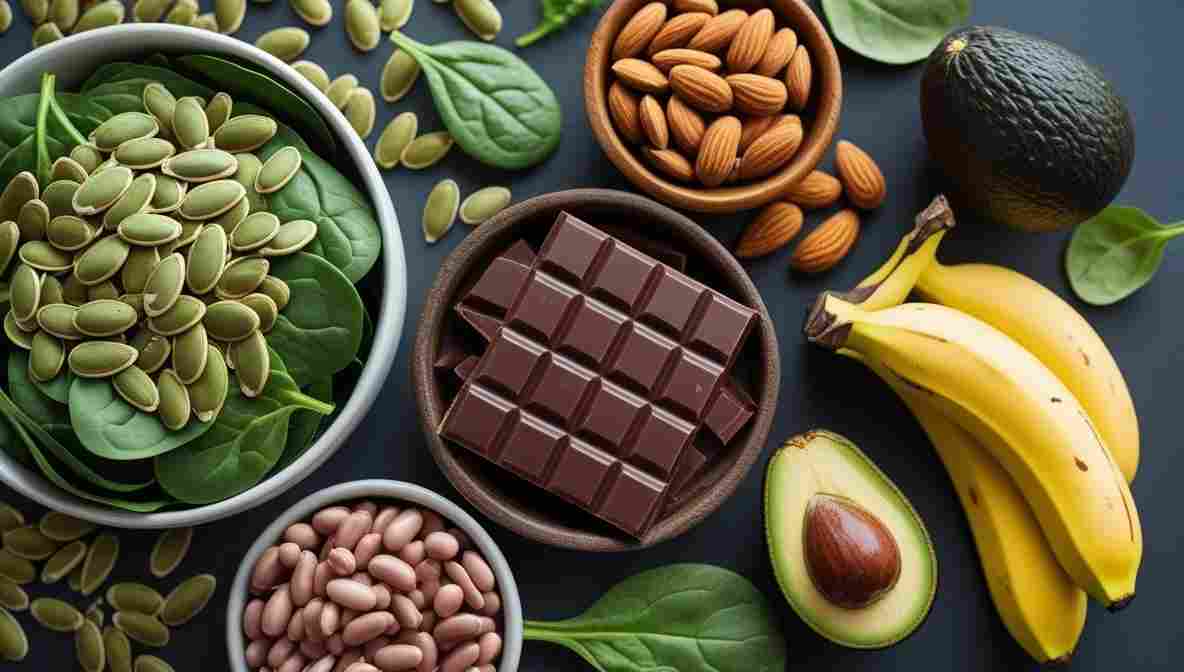
🥦 Best Magnesium-Rich Foods for Mental Health
You don’t always need supplements—your kitchen can be your medicine cabinet. Here are some excellent natural sources of magnesium:
| Food | Magnesium Content (mg per 100g) |
|---|---|
| Pumpkin seeds (Pepitas) | 534 mg |
| Spinach (cooked) | 87 mg |
| Almonds | 270 mg |
| Dark chocolate (70-85% cocoa) | 228 mg |
| Avocados | 29 mg |
| Bananas | 27 mg |
| Black beans | 171 mg |
Related:
💊 Should You Take Magnesium Supplements?
For individuals with magnesium deficiency or high stress levels, supplements may be helpful. Common forms include:
- Magnesium glycinate: Best for anxiety and sleep
- Magnesium citrate: Gentle on digestion
- Magnesium L-threonate: Crosses the blood-brain barrier, may support memory and cognition
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplements, especially if you are already on medication for depression or anxiety.
Also Read: Magnesium for Dementia and Cognitive Health
🛑 Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency
Low magnesium can mimic or worsen mental health symptoms. Watch for:
- Muscle cramps and twitches
- Fatigue or weakness
- Irritability or nervousness
- Trouble sleeping
- Frequent headaches
If you’re experiencing these symptoms, it may be time to evaluate your magnesium intake.
🧘 Lifestyle Tips to Maximize Magnesium’s Mental Health Benefits
Pairing magnesium with healthy habits enhances its effect:
- Exercise regularly: boosts mood and helps regulate magnesium levels
- Reduce sugar and alcohol: both deplete magnesium stores
- Prioritize gut health: chronic stress weakens the immune system and disrupts nutrient absorption
- Practice mindfulness or yoga: supports relaxation and enhances mineral balance
Learn about yoga exercises for dementia, also helpful for anxiety management.
💡 Final Thoughts
So, does magnesium really help with anxiety and depression? The answer is a strong yes—especially when paired with proper lifestyle changes. Magnesium plays a vital role in regulating mood, calming the nervous system, improving sleep, and supporting brain function.
Whether through diet or supplements, prioritizing magnesium intake is a simple yet effective step toward better mental health. In a world filled with stress, this underrated mineral might just be your natural ally in achieving emotional balance.
🔍 FAQs
1. Can magnesium be used instead of antidepressants?
Magnesium can complement treatment but should not replace prescribed medications without medical supervision.
2. How long does it take for magnesium to help anxiety?
Many people report improvement within 1–6 weeks of regular intake.
3. What form of magnesium is best for mental health?
Magnesium glycinate or L-threonate are commonly used for anxiety and cognitive function.
4. Can you get enough magnesium from food alone?
Yes, with a balanced diet rich in leafy greens, seeds, and nuts, many people can meet their needs naturally.
5. Is magnesium safe for long-term use?
Yes, when taken at recommended doses, magnesium is safe for long-term health.
6. Does magnesium help with sleep?
Absolutely. It promotes relaxation and supports deeper, more restful sleep.
7. Can magnesium help teenagers with anxiety?
It may help, but always consult a pediatrician before supplementation.
8. Are there any side effects of magnesium?
Too much can cause diarrhea or stomach upset. Stick to recommended dosages.
9. How is magnesium related to the stress hormone?
It helps regulate cortisol levels, reducing chronic stress impacts on the body.
10. Can magnesium help people with both dementia and depression?
Yes. Magnesium may benefit cognitive function and mood in older adults.