Exploring the role of methadone in the management of neuropathic pain: a comprehensive guide.
Basic scientific data indicates that methadone inhibits or interferes with the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin, like modern antidepressants. Including antidepressants proven to be very effective in managing or preventing neuropathic pain, such as duloxetine and venlafaxine. Additionally, methadone binds to the NMDA receptor, which is a recognized modulator of neuropathic pain.
Neuropathic pain is a very complex and often debilitating condition. Which results from damage or dysfunction of the nervous system. Conventional painkillers do not always provide us with adequate pain relief. Due to which researchers and physicians have to find other or alternative medicines. Someone chooses some other medicine instead.
Methadone, a synthetic narcotic fundamentally known for its role in the treatment of narcotic addiction, has, as of late, acquired consideration for its possible use in the administration of neuropathic torment.
In this article, we will make exhaustive sense of the components of neuropathic torment, the special properties of methadone, and its adequacy in giving help to people experiencing this difficult condition.
Methadone structure:
Methadone has a specific chemical structure. Which differentiates it from traditional opioids by being classified as an open-chain amine. In methadone specifically, it falls into the category of diphenylheptane.
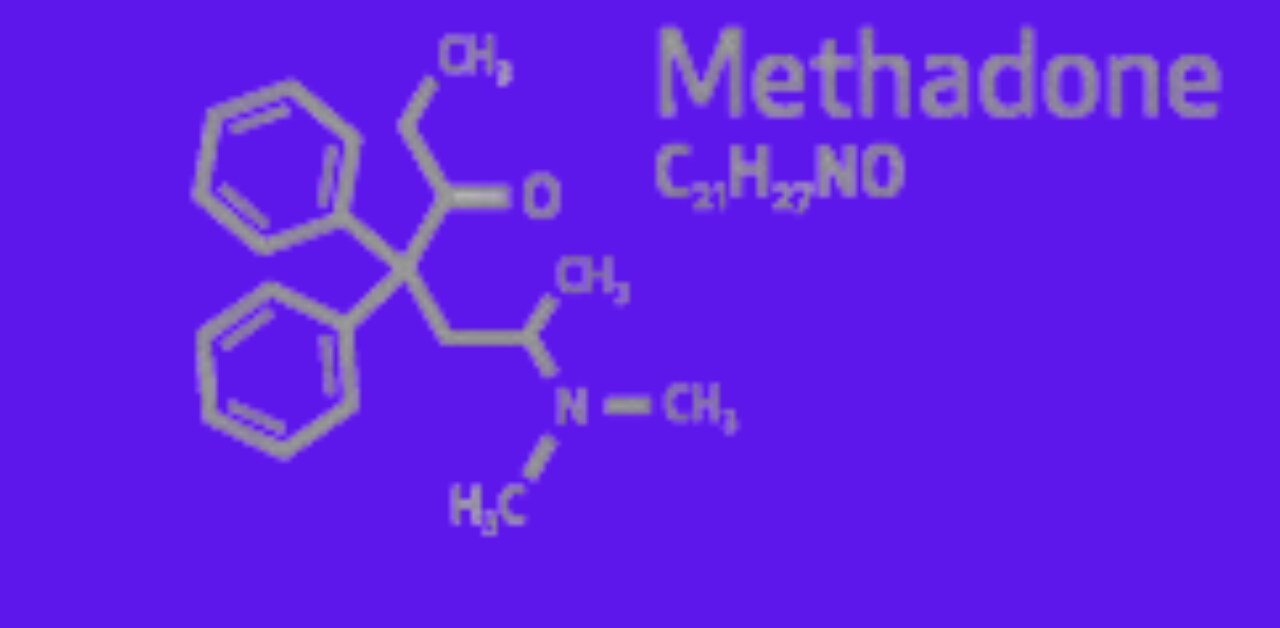
The creation of the D and L isomers is facilitated by this special structural conformation, which is defined by the presence of an asymmetric carbon and an open chain. These isomers differ significantly in how they function at the NMDA and opioid receptors. In the United States, the prevalent form of methadone is racemic, which contains both D and L isomers. In contrast, in Germany, the L isomer is predominantly used as the primary form. The complex pharmacological effects of methadone are strongly influenced by its structural diversity. Which highlights the wide application and importance of methadone in different medical conditions.
Composition:
Methadone hydrochloride is a lipid-soluble opioid. And it is available as oral tablets, oral elixirs, and solutions for administration by intravenous (IV) injection or rectally.
Compatibility or integration:
Methadone is physically compatible with many of the medications used in palliative care. Such as dexamethasone, hyoscine Butylbromide (it is not available in the United States), ketorolac, methotrimeprazine, and midazolam.
Methadone administration routes and pharmacology:
Methadone has been administered by oral, IV, rectal, subcutaneous, sublingual, and intrathecal routes. Knowledge of the effects of methadone given by non-oral routes is important in palliative care. Because when the patient is in a dying state, he cannot take the medicine orally.
Understanding Neuropathic Pain:
Neuropathic pain is characterized by abnormal sensory processing in the peripheral or central nervous system. General conditions leading to neuropathic pain. Including diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and nerve compression injuries. This type of pain is often described as burning, shooting, or electric shock-like sensations. And this can have a very essential impact on the quality of any person’s life.
Role of methadone and neuropathic pain:
Methadone, which was originally developed as an analgesic, Methadone has gotten great, boundless acknowledgment for its viability in treating narcotic fixation. Luckily, it likewise gave an elective choice to getting neuropathic torment due to its unique restorative properties. Methadone acts as a mu-opioid receptor agonist. But it also exhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist properties. Its dual mode of action makes it different from other opioids. This may improve the ability to reduce or cure neuropathic pain.
Mechanisms of methadone in neuropathic pain:
Mu-opioid receptor agonism: The primary action of methadone involves binding to mu-opioid receptors, reducing the transmission of pain signals, and modulating pain perception. This mechanism is common in traditional opioids. But methadone’s potency and very long half-life contribute to its consistently providing pain relief.
NMDA receptor antagonism: Methadone’s NMDA receptor antagonism distinguishes it from many other opioids. By inhibiting NMDA receptors, methadone can prevent or suppress the emerging development of hyperalgesia and allodynia, two phenomena commonly associated with neuropathic pain.
Clinical Studies and Efficacy:
Various examinations have analyzed the adequacy or security of methadone in the alleviation of neuropathic pain. Be that as it may, we really want more examination to reach or lay out authoritative determinations.
Preliminary discoveries propose that methadone might give viable help to certain people experiencing neuropathic torment. Particularly methadone for individuals who don’t respond satisfactorily to other agony-easing drugs.
Considerations and precautions:
Despite its potential advantages, the utilization of methadone in neuropathic pain management requires careful consideration. Individual patient factors, including medical history. Coexisting conditions, and risk of addiction, should be thoroughly evaluated. Moreover, medical care suppliers ought to screen patients to limit the potential for unfriendly impacts and guarantee ideal agony control.
conclusion:
Methadone’s dual component of activity as a mu-opioid receptor agonist and NMDA receptor antagonist makes it an interesting contender for neuropathic pain in officers. While more research is needed to officially prove its efficacy. Current evidence suggests that methadone may offer a powerful alternative for people struggling with neuropathic pain. Like any clinical intervention, thorough evaluation by medical service experts is important to create therapy designs and improve outcomes for patients.
Here are some question and answer of Methadone and neuropathic pain:
How does methadone help with pain?
- Methadone, which was originally developed as an analgesic. Methadone has gotten great, boundless acknowledgment for its viability in treating narcotic fixation. Luckily, it likewise gave an elective choice to getting neuropathic torment due to its unique restorative properties.
- Methadone acts as a mu-opioid receptor agonist. But it also exhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist properties. Its dual mode of action makes it different from other opioids. This may improve the ability to reduce or cure neuropathic pain.
Does methadone help diabetic neuropathy?
- Neuropathic pain is characterized by abnormal sensory processing in the peripheral or central nervous system.
- General conditions leading to neuropathic pain. Including diabetic neuropathy, post-herpetic neuralgia, and nerve compression injuries.
- This type of pain is often described as burning, shooting, or electric shock-like sensations. And this can have a very essential impact on the quality of any person’s life.